CMA vs Series 7
CMA and Series 7 represent two distinct paths in finance with virtually no career overlap. CMA certifies expertise in management accounting - working INSIDE corporations analyzing financial performance, creating budgets, and advising executives on business decisions. Series 7 licenses securities representatives to work OUTSIDE corporations selling investments to clients at broker-dealers. CMAs never need Series 7 for their work; Series 7 holders never need CMA for theirs. The comparison helps those choosing between corporate finance vs. investment sales careers.
Side-by-Side Comparison
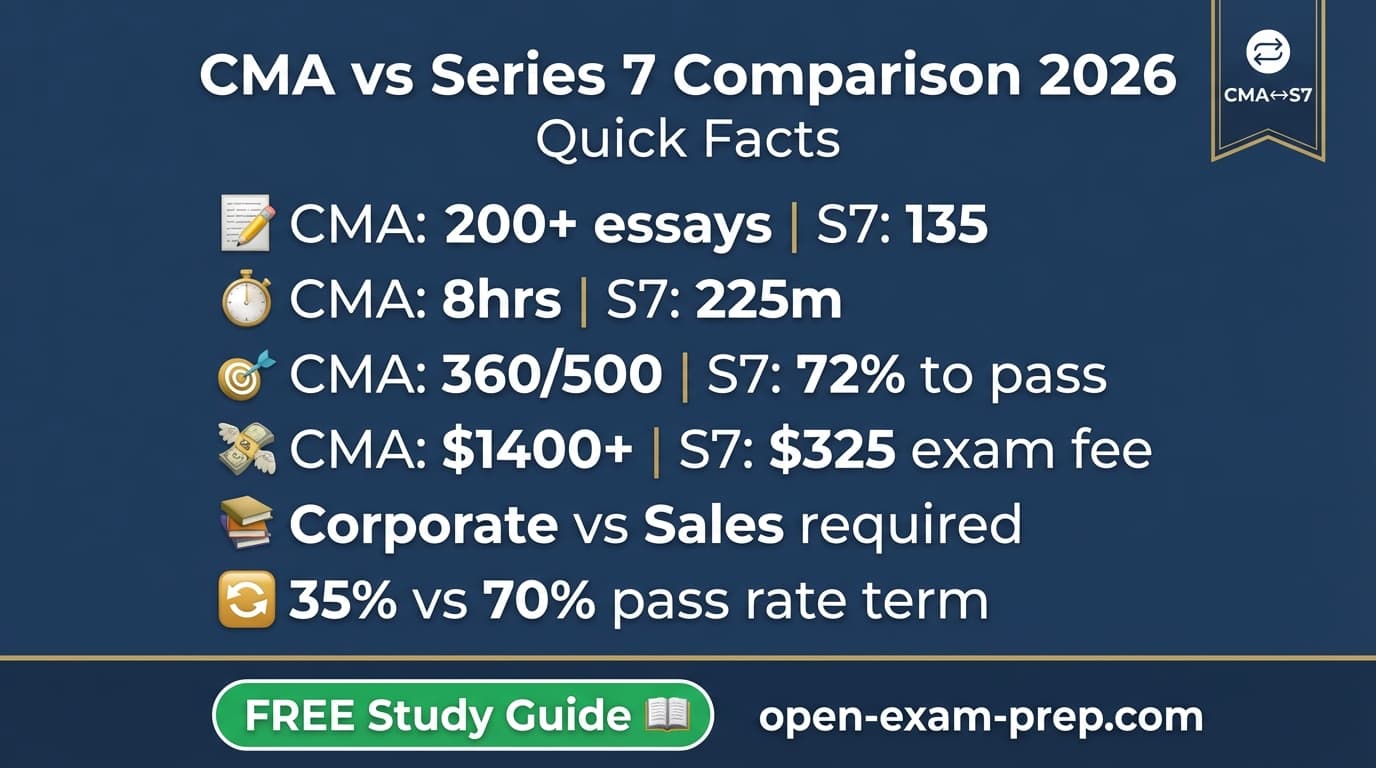
| Feature | CMA | Series 7 |
|---|---|---|
| Full Name | Certified Management Accountant | General Securities Representative |
| Exam Cost | $545/part ($1,090 total) + membership | $245 (+ $80 SIE) |
| Passing Score | 360/500 (scaled) | 72% |
| Questions | 100 MCQ + 2 essays per part | 135 (125 scored + 10 unscored) |
| Time Limit | 4 hours per part (8 hours total) | 225 minutes |
| Study Time | 300-400 hours | 80-120 hours |
| Difficulty | Very Challenging | Challenging |
| Prerequisites | Bachelor's degree + 2 years management accounting experience | SIE exam + firm sponsorship |
| Exam Body | IMA (Institute of Management Accountants) | FINRA |
Key Differences
- 1CMA is for corporate finance/accounting; Series 7 is for investment sales
- 2CMA works inside companies; Series 7 works at broker-dealers serving clients
- 3CMA has essay questions; Series 7 is all multiple-choice
- 4CMA requires bachelor's + 2 years experience; Series 7 requires firm sponsorship
- 5CMA costs $1,400-1,700 total; Series 7 path costs $325
- 6CMA pass rate is 35-45%; Series 7 pass rate is ~70%
What Each Exam Allows You To Do
CMA
- Lead financial planning and analysis
- Perform cost management
- Support strategic decisions
- Advance to Controller/CFO roles
Series 7
- Sell stocks, bonds, and options
- Sell mutual funds and ETFs
- Work as registered representative
- Advise clients on investments
Who Should Take Each Exam?
Take the CMA if you...
- →Corporate finance professionals
- →FP&A analysts
- →Management accountants
- →Those on CFO track
Take the Series 7 if you...
- →Stockbrokers and advisors
- →Wirehouse representatives
- →Those in securities sales
- →Investment firm careers
Which Should You Take First?
Choose based on your career direction - these don't complement each other. If you want to work in corporate finance analyzing business performance, creating forecasts, and eventually becoming a Controller or CFO, pursue CMA. If you want to help individuals invest their money, work at investment firms, and potentially earn commission-based income, pursue Series 7. These are fundamentally different careers with different skills, compensation structures, and work environments.
Frequently Asked Questions
QCan having both CMA and Series 7 help my finance career?
Rarely, because they serve completely different functions. A CMA doing FP&A inside a company would never use a Series 7 license. A Series 7 broker selling investments would never use CMA cost accounting skills. The only possible overlap: someone at an investment firm's internal finance department might theoretically benefit, but this is extremely uncommon. Focus your time and money on the certification that matches your actual career path.
QWhich is harder - CMA or Series 7?
CMA is significantly harder. The CMA has a 35-45% pass rate versus ~70% for Series 7. CMA requires 300-400 hours of study across two 4-hour exams that include essay questions. CMA content requires deep understanding of financial analysis, cost accounting, and business strategy. Series 7 requires 80-120 hours of study for a single 225-minute multiple-choice exam. Both are challenging, but CMA's difficulty and comprehensiveness exceed Series 7.
QWhich offers higher earning potential?
Both can reach six figures with different trajectories. CMAs average $90,000-$120,000, with senior positions (Controller, VP Finance, CFO) earning $150,000-$400,000+. Series 7 representatives have variable income based on sales - averages are $60,000-$90,000, but top producers at major firms earn $200,000+. CMA offers more predictable salary growth; Series 7 offers more variability with higher upside for top salespeople and advisors who build large client books.
QWhat's the day-to-day difference between these careers?
CMAs spend their days analyzing financial data, building Excel models, creating budgets and forecasts, preparing management reports, and advising executives on business decisions. Work is analytical, internal-facing, and typically 40-50 hour weeks. Series 7 representatives spend their days prospecting for clients, meeting with investors, recommending investment strategies, executing trades, and building client relationships. Work is sales-oriented, client-facing, and hours can vary with market conditions.
10 free AI interactions per day
Ready to Start Studying?
Free study materials for both exams - start learning today.
Related Exam Comparisons
Stay Updated
Get free exam tips and study guides delivered to your inbox.